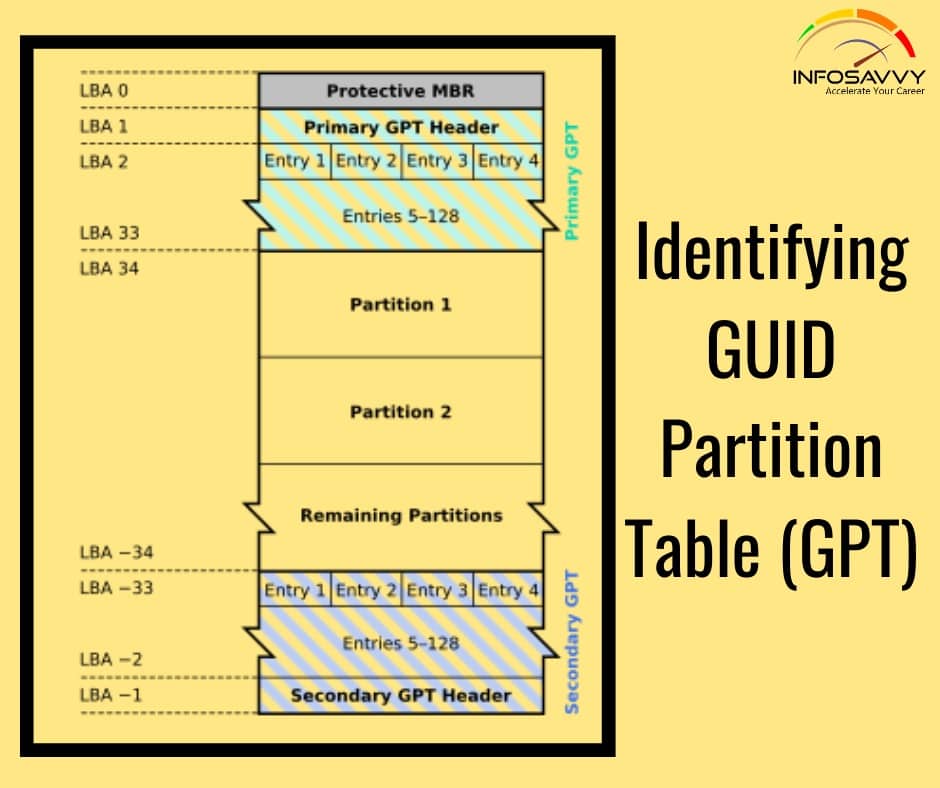
Identifying GUID Partition Table (GPT) in this GPT header will help an investigator analyze the layout of the disk including the locations of the partition table, partition area, and backup copies of the header and partition table. Investigators can use cmdlets given below in Windows PowerShell to identify the presence of GPT:
Get-GPT
Get-GPT command helps investigator to analyze the GUID Partition Table data structure of the hard disk. It requires the use of the -Path parameter which takes the Win32 Device Namespace (ex.\\.\ PHYSICALDRIVE1) for the device from which it should parse the GPT.
In case, the investigator uses the Get-CPT on a disk formatted with a Master Boot Record, it will display an error message prompting to use Get-MBR instead.
Alternate Method:
- Open “Computer Management” application and click “Disk Management” on the left pane. Right-click on the primary disk (here, Disk 0) and then click Properties
- In the Device Properties window, click ‘Volumes” tab to see the Partition style
Related Product : Computer Hacking Forensic Investigator | CHFI
Identifying GUID Partition Table (GPT) (Cont’d)
1. Get-Boot Sector
The Get-BootSector is a command that can help the investigator parse GPTs of both types of hard disks including the ones formatted with either UEFI or MBR. This command acts as replacement for Get-MBR and Get-GPT cmdlets. Get-BootSector analyzes the first sector of hard drive and determines the formatting type used and then parses the hard drive GPT.
2. Get-PartitionTable
This command analyzes the GUID partition table to find the exact type of boot sector (Master Boot Record or GUID PartitionTable) and displays the partition object.
3. Analyzing the GPT Header and Entries
Most of the operating systems that support GPT disk access come up with a basic partitioning tool, which displays details about CPT partition tables. In windows tools such as DiskPart tool display the partition details, whereas MAC systems use the OS X Disk utility and Linux uses GNU parted tool.
Sleuthkit mmls command can help the investigators to view detailed partition layout for GPT disk along with the MAR details. Alternatively, investigators can gather details about GPT header and partition entries through manual analysis of disk drive using a hex calculation or editing tool called Hex editor.
Also Read : What is the Booting Process?
4. GPT Artifacts
Deleted and Overwritten GUID Partitions
Case 1: In hard disks, the conversion or repartition of the MBR disk to GPT will generally overwrite the sector zero with a protective MBR, which will delete all the information about the old partition table. The investigators should follow the standard forensics methods of searching the filesystems to recover data about the previous MBR partitioned volumes.
Case 2: When conversion or repartition of the GPT to MBR disk takes place, then the GPT header and tables may remain intact based on the tool used. Investigators can easily recover or analyze data of such disk partitions.
Implementation of general partition deletion tools for deletion of partition on the GPT disk might will delete the protective MBR only, which investigators can easily recreate by simply reconstructing the disk.
As per UEFI
specification, if all the fields in a partition entry have zeroed values, it implies that the entry is not in use. In this case, data recovery about deleted GUID partition entries is not possible.
Read More : https://info-savvy.com/identifying-guid-partition-table-gpt/
This Blog Article is posted by
Infosavvy, 2nd Floor, Sai Niketan, Chandavalkar Road Opp. Gora Gandhi Hotel, Above Jumbo King, beside Speakwell Institute, Borivali West, Mumbai, Maharashtra 400092
Contact us – www.info-savvy.com
